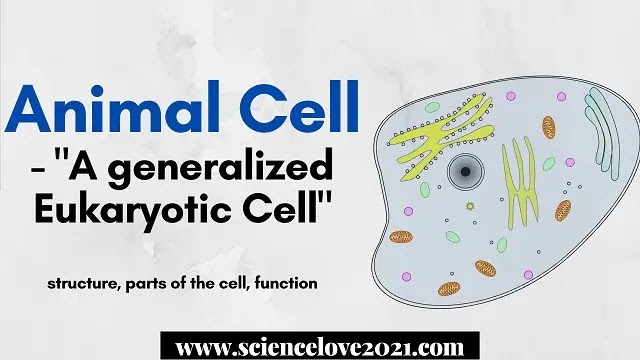
Cell structure
- It is a generalized Eukaryotic animal Cell.
- Cell wall is not found in it.
- Plasma membrane marks the boundary of Cell and possess desmosomes and microvilli.
- Chloroplasts and vacuole not found.
- Cell Organelles like Mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, Ribosomes, Lysosomes centrosome, nucleous and nucleolus etc are present.
- The genetic material DNA is confined on the centrosome found usually in the nucleus.
- Pinocytic and secretory vesicles are seen.
- Cell shape definite.
Part of the Cell
A. Plasma Membrane
- Plasma membrane is thin, flexible, living and semi permeable membrane.
- In plant cell one extra cell wall present outside of the Plasma lemma.
- Plasma membrane is a unit membrane.
- It is composed of a unit membrane.
- It surrounds the protoplasm.
Function
- It protect the cytoplasm and other cell organelles from external injuries.
- It gives mechanical support to animal cells.
- In Plasma membrane regeneration is found.
B. Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is a viscous homogeneous, granular living material and surrounded the nucleus of the cell.
Cytoplasm divided into three parts-
- Plasma membrane
- Tonoplast
- Plasma membrane and center part of Tonoplast
Function
- Many enzyme actions take place in it.
- It provides a medium for cell organelles and inclusion to float and perform the life processes.
C. Endoplasmic reticulum
- It is found in all eukaryotic cells except RBCs and mature egg cells.
- Endoplasmic reticulum is secretory cells like pancreas, liver and endocrine glands are highly developed.
- It was first reported by K.R. Porter in 1948.
- It is a network of tubules, cisterane and vesicles traversing in the cytoplasm cisternal membrane are interconnected by interconnecting tubules.
- Endoplasmic reticulum is either smooth or rough the tubular surface of smooth Endoplasmic reticulum are devoid of ribosomes, while those with ribosomes are rough or granular Endoplasmic reticulum.
- E.R. provides mechanical support to the cell.
- E.R. also gives rise to the other membrane structure of the cell Like structure and nuclear membrane and helps in conducting intracellular information.
Function
- It provides mechanical support to the cell.
- It forms the endoskeleton and communicative network of the cell.
D. Mitochondria
- Mitochondria is discovered by Kolliker in 1880.
- It is described by Altmann in 1890 & turm Mitochondria given by C. Benda in 1897 to the bioblast of Altman.
- Mitochondria vary in shape from spherical to rod shaped.
- They are living and are surrounded by two membrane, the inner wall being folded to form the cristae.
- The cristae bear several F1 particles.
- The Mitochondria are said to be originated from E.R. .
Function
- The Mitochondria is called the Power house of the cell because they release energy by the oxidation of food stuffs and store in the form of ATP.
E. Ribosomes
- In animal Cell it is discovered by Palade in 1955.
- Ribosomes are minute spherical bodies attached to the Endoplasmic reticulum or dispersed freely in the cytoplasm of both plant and animal cells.
- In the bases of sedimentation coefficient the ribosomes are two types-
- 70 S ribosomes (small in size)
- 80 S ribosomes (large in size)
Function
They are sites for protein synthesis from amino acids.
F. Golgi complex
- Golgi complex is formed of stacks of cisterane, vesicles and vacuole.
- It was reported by Camillo Golgi in 1891.
- The position of Golgi complex is definite in animal cells.
- Lysosomes are believed to be formed from Golgi complex.
Function
- It secretes hormones and enzymes.
- It give rise to acrosome of sperm during the process of spermiogenesis.
- The secretory cell process much active Golgi complex.
G. Lysosomes
- It was discovered by de Duve in 1955.
- Lysosomes are sac like structure containing digestive enzymes.
- Lysosomes are formed with Golgi bodies or E.R..
- Those Lysosomes which are formed with Golgi bodies or E.R. are called primary Lysosomes.
Function
- They help in digestion of food particles and are called suicidal bag.
- They help in the cell division.
Centrosome with centrioles
- Centrosome are non-membranous small and hollow cylinder present in a space.
- Turm Centrosome is used by T. Boveri in 1888.
Function
They help in the movement of chromatids during cell division.
H. Nucleus
- It was discovered by Robert brown in 1831.
- It is a dense and spherical living body containing the hereditary material, chromosomes.
- It is formed of two membranes which are separated by perinuclear space.
- The protoplasm of Nucleus is known as Nucleoplasm.
- In Nucleus a small circle like part present which is known as Nucleolus and it was discovered by Fontana in 1781.
Function
It control all the vital activities of the cell and carries hereditary material from generation to generation.
I. Vacuole
Vacuole is a non-living clear cavity containing watery cell sap.
The outer layer of a vacuole is called Tonoplast.
Function
It stores water minerals and food in the form of simple sugar and waste products.

.webp)
No comments:
Post a Comment